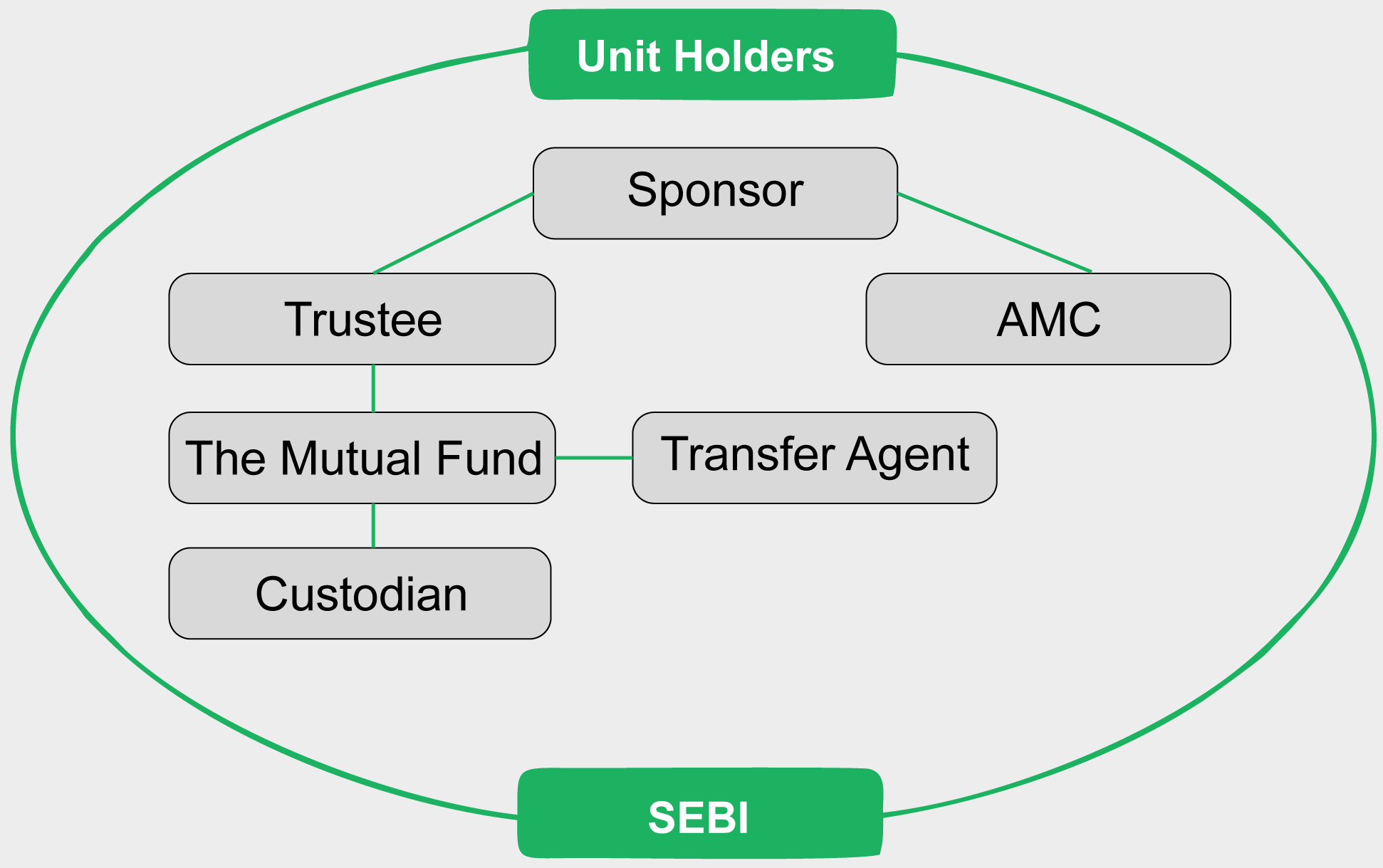
1) Sponsors
The application to SEBI for registration of a mutual fund is made by the sponsor/s. Thereafter, the sponsor invests in the capital of the AMC.
Since sponsors are the main people behind the mutual fund operation, eligibility criteria has been specified as follows:
The sponsor should have a sound track record and reputation of fairness and integrity in all business transactions. The requirements are:
o Sponsor should be carrying on business in financial services for not less than 5 years.
o Sponsor should have positive net worth (share capital plus reserves minus accumulated losses) in all the immediately preceding 5 years
o Net worth in the immediately preceding year should be more than the amount that the sponsor contributes to the capital of the AMC
o The sponsor should have earned profits, after providing for depreciation and interest and tax, in three of the previous five years, including the latest year.
The sponsor should be a fit and proper person for this kind of operation.
The sponsor needs to contribute a minimum 40 percent of the net worth of the AMC. Further, anyone who holds 40 percent or more of the net worth of share-holding in the AMC is considered to be a sponsor, and should therefore fulfill the eligibility criteria mentioned above.
Sponsors have to contribute a minimum of Rs.1,00,000 as initial contribution to the corpus of the mutual fund.
In the example of SBI Mutual Fund cited above, the sponsor is State Bank of India, an Indian public sector bank. Sponsorship may be institutional (LIC Nomura Mutual Fund), entirely foreign (like Franklin Templeton Mutual Fund and Goldman Sachs Mutual Fund), predominantly foreign joint venture (like JP Morgan Mutual Fund & HSBC Mutual Fund) or predominantly Indian joint venture (like Birla Sun Life Mutual Fund & ICICI Prudential Mutual Fund).
2) Trustee
The trustees have a critical role in ensuring that the mutual fund complies with all the regulations, and protects the interests of the unit-holders.
The SEBI Regulations stipulate that:
Every trustee has to be a person of ability, integrity and standing A person who is guilty of moral turpitude cannot be appointed trustee.
A person convicted of any economic offence or violation of any securities laws cannot be appointed as trustee
No AMC and no director (including independent director), officer, employee of an AMC shall be eligible to be appointed as a trustee of a mutual fund
No person who is appointed as a trustee of a mutual fund shall be eligible to be appointed as trustee of any other mutual fund.
Prior approval of SEBI needs to be taken, before a person is appointed as Trustee.
The sponsor will have to appoint at least 4 trustees. If a trustee company has been appointed, then that company would need to have at least 4 directors on the Board. Further, at least two-thirds of the trustees / directors on the Board of the trustee company would need to be independent trustees i.e. not associated with the sponsor in any way.
SEBI expects Trustees to perform a key role in ensuring legal compliances and protecting the interest of investors. Accordingly, various General Due Diligence and Special Due Diligence responsibilities have been assigned to them. The rights and responsibilities include the following:
• Enter into an Investment Management Agreement with the AMC that will define the functioning of the AMC in making and managing the mutual fund’s investments.
• The trustees have the right to seek any information they require from the AMC to facilitate meeting their responsibilities as trustees.
• The trustees shall ensure before the launch of any scheme that all the key personnel and associates such as fund managers, compliance officer, R&T agent, auditors and others have been appointed and all systems are in place.
• The trustees shall periodically review the service contracts entered into for custody arrangements, transfer agency and others and ensure they are in the interest of the unitholders and that all service providers are registered with SEBI.
• They shall ensure that all transactions entered into by the AMC are in compliance with the regulations and the scheme’s objectives and intent.
• The trustees shall ensure that the interests of the unitholders are not compromised in any of the AMC’s dealings with brokers, other associates and even unitholders of other schemes.
• If the trustees believe that the conduct of the business of the mutual fund is contrary to the provisions of the regulations, then they must take corrective action and inform SEBI of the same.
• The trustees shall not permit a change in the fundamental attributes of the scheme, the trust or fees and expenses or any other change that will affect the interests of the unit holders unless a written communication is sent to each unitholder, a notice is given in the newspaper with national circulation and the unitholders are given the option to exit at NAV without paying an exit load.
• Trustees have to file details of their securities dealings on a quarterly basis with the mutual fund • On a quarterly basis the trustees shall review the transactions of the mutual fund with the AMC and its associates. They shall also review the net worth of the AMC on a quarterly basis and ensure that any shortfall is made up.
• The trustees shall periodically review the investor complaints received and their redressal by the AMC.
• They shall ensure that the trust property is properly protected, held and administered.
• The trustees shall obtain and consider the reports of the auditors and compliance officers in their periodic meetings and take action as required.
• Make half-yearly reports to SEBI
The strict provisions go a long way in promoting the independence of the role of trusteeship in a mutual fund.
3) Asset Management Company (AMC)
Day to day operations of asset management is handled by the AMC. The sponsor or, the trustees if so authorized by the trust deed, shall appoint the AMC with the approval of SEBI.
As per SEBI regulations:
The directors of the asset management company need to be persons having adequate professional experience in finance and financial services related field
The directors as well as key personnel of the AMC should not have been found guilty of moral turpitude or convicted of any economic offence or violation of any securities laws.
Key personnel of the AMC should not have worked for any asset management company or mutual fund or any intermediary during the period when its registration was suspended or cancelled at any time by SEBI.
Prior approval of the trustees is required, before a person is appointed as director on the board of the AMC.
Further, at least 50 percent of the directors should be independent directors i.e. not associate of or associated with the sponsor or any of its subsidiaries or the trustees.
The AMC needs to have a minimum net worth of Rs. 50 crore.
A change in the controlling interest of the AMC can be made only with the prior approval of the trustees and SEBI. A written communication about the change in the controlling interest of the AMC is sent to each unitholder and an advertisement is given in one English daily newspaper having nationwide circulation and in a newspaper published in the language of the region where the Head Office of the mutual fund is situated. The unitholders are given the option to exit at NAV without paying an exit load.
The AMC is responsible for conducting the activities of the mutual fund. It therefore arranges for the requisite offices and infrastructure, engages employees, provides for the requisite software, handles advertising and sales promotion, and interacts with regulators and various service providers.
The AMC has to take all reasonable steps and exercise due diligence to ensure that the investment of funds pertaining to any scheme is not contrary to the provisions of the SEBI regulations and the trust deed. Further, it has to exercise due diligence and care in all its investment decisions.
The appointment of an AMC can be terminated by a majority of the trustees, or by 75 percent of the Unit-holders. However, any change in the AMC is subject to prior approval of SEBI and the Unit-holders.
Operations of AMCs are headed by a Managing Director, Executive Director or Chief Executive Officer. Some of the other business-heads are:
Chief Investment Officer (CIO), who is responsible for overall investments of the fund. Fund managers assist the CIO. As per SEBI regulations, every scheme requires a fund manager, though the same fund manager may manage multiple schemes.
Securities Analysts support the fund managers through their research inputs. As will be discussed in Chapter8, these analysts come from two streams—Fundamental Analysis and Technical Analysis. Some mutual funds also have an economist to analyse the economy.
Securities Dealers help in putting the transactions through the market. The mutual fund schemes’ sale and purchase of investments are executed by the dealers in the secondary market.
Chief Marketing Officer (CMO), who is responsible for mobilizing money under the various schemes. Direct Sales Team (who generally focus on large investors), Channel Managers (who manage the distributors) and Advertising & Sales Promotion Team support the CMO.
Chief Operations Officer (COO) handles all operational issues.
Compliance Officer needs to ensure all the legal compliances. In Offer Documents of new issues, he signs a due-diligence certificate to the effect that all regulations have been complied with, and that all the intermediaries mentioned in the offer document have the requisite statutory registrations and approvals.
In order to ensure independence, the Compliance Officer reports directly to the head of the AMC. Further, he works closely with the Trustees on various compliance and regulatory issues.
AMCs are required to invest seed capital of 1percent of the amount raised subject to a maximum of Rs.50 lakh in all the growth option of the mutual fund schemes through the lifetime of the scheme.
Other Service Providers
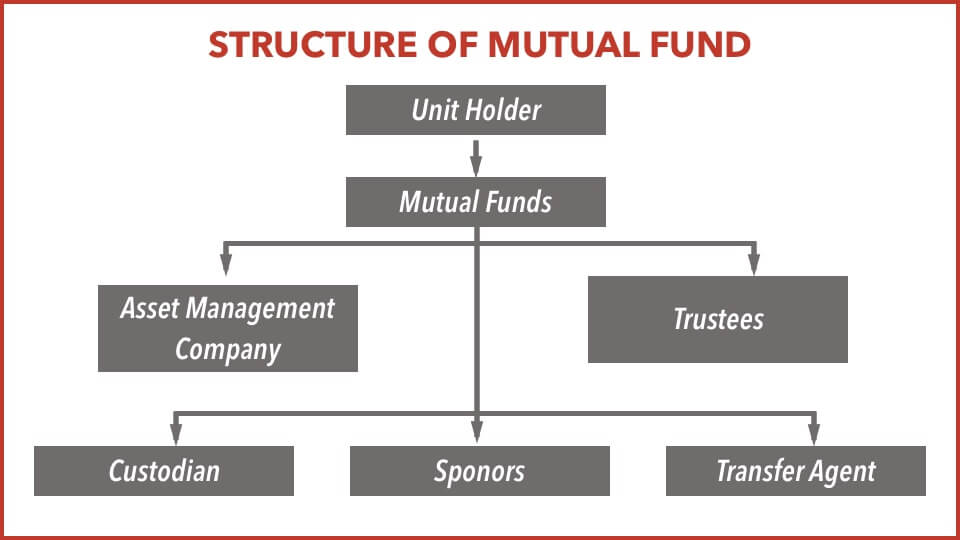
4) Custodian
The custodian has custody of the assets of the fund. As part of this role, the custodian needs to accept and give delivery of securities for the purchase and sale transactions of the various schemes of the fund. Thus, the custodian settles all the transactions on behalf of the mutual fund schemes.
All custodians need to register with SEBI. The Custodian is appointed by the trustees. A custodial agreement is entered into between the trustees and the custodian.
The SEBI regulations provide that if the sponsor or its associates control 50 percent or more of the shares of a custodian, or if 50 percent or more of the directors of a custodian represent the interest of the sponsor or its associates, then, unless certain specific conditions are fulfilled, that custodian cannot be appointed for the mutual fund operation of the sponsor or its associate or subsidiary company.
An independent custodian ensures that the securities are indeed held in the scheme for the benefit of investors – an important control aspect.
The custodian also tracks corporate actions such as dividends, bonus and rights in companies where the fund has invested.
5) RTA
The RTA maintains investor records. Their offices in various centres serve as Investor Service Centres (ISCs), which perform a useful role in handling the documentation of investors. The functions of the RTA includes processing of purchase and redemption transactions of the investor and dealing with the financial transactions of receiving funds for purchases and making payments for redemptions, updating the unit capital of the scheme to reflect these transactions, updating the information in the individual records of the investor, called folios, keeping the investor updated about the status of their investment account and information related to the investment.
The appointment of RTA is done by the AMC. It is not compulsory to appoint a RTA. The AMC can choose to handle this activity in-house. All RTAs need to register with SEBI.
6) Auditors
Auditors are responsible for the audit of accounts.
Accounts of the schemes need to be maintained independent of the accounts of the AMC.
The auditor appointed to audit the scheme accounts needs to be different from the auditor of the AMC.
While the scheme auditor is appointed by the Trustees, the AMC auditor is appointed by the AMC.
7) Fund Accountants
The fund accountant performs the role of calculating the NAV, by collecting information about the assets and liabilities of each scheme. The AMC can either handle this activity in-house, or engage a service provider. There is no need for a registration with SEBI to perform this function.
8) Distributors
Distributors have a key role in selling suitable types of units to their clients i.e. the investors in the schemes of mutual funds with whom they are empanelled. A distributor can be empanelled with more than one mutual fund. Distributors can be individuals or institutions such as distribution companies, broking companies and banks.
9) Collecting Bankers
The investors’ money go into the bank account of the scheme they have invested in. These bank accounts are maintained with collection bankers who are appointed by the AMC.
Leading collection bankers make it convenient to invest in the schemes by accepting applications of investors in most of their branches. Payment instruments against applications handed over to branches of the AMC or the RTA need to be banked with the collecting bankers, so that the money is available for investment by the scheme. Thus, the banks enable collection and payment of funds for the schemes.
Through this kind of a mix of constituents and specialized service providers, most mutual funds maintain high standards of service and safety for investors.
10) KYC Registration Agencies
To do away with multiple KYC formalities with various intermediaries, SEBI has mandated a unified KYC for the securities market through KYC Registration Agencies registered with SEBI. Any new investor, Joint holders, Power of Attorney holders, Donors and Guardian (in case of minors) have to comply with the KYC formalities. In-Person Verification (IPV) by a SEBI-registered intermediary is compulsory for all investors. However, the investor needs to get IPV done by only one SEBI-registered intermediary (broker, depository, mutual fund distributor etc.). This IPV will be valid for transactions with other SEBI-registered intermediaries too.
Distributors who have a valid NISM-Series-V-A: Mutual Fund Distributors certificate and a valid ARN can carry out the In-person verification if they have completed the KYD process.
11) Payment Aggregators
Payment Aggregators such as Tech Process, Bill Desk are payment providers in the online market place. Payment aggregators enable the users to make the payments online through their existing bank account in a secured and a convenient manner.
Aggregators allow mutual fund houses to accept credit card and bank transfers without having to setup a merchant account with the banks. The aggregator provides the means for facilitating payment from the consumer via credit cards or bank transfer to the mutual fund. The mutual fund is paid by the aggregator.
No comments:
Post a Comment